1번. 배열의 값에 각 2배의 연산된 값이 산출되도록 메소드를 작성하시오.
int num1[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// num1 = getDouble(num1);
getDouble(num1);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(num1));
1번 문제 풀이
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Homework1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num1[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
getDouble(num1);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(num1));
}
static int[] getDouble(int num[]){
for(int i = 0 ; i < num.length ; i++) {
num[i] = num[i] * 2;
}
return num;
}
}
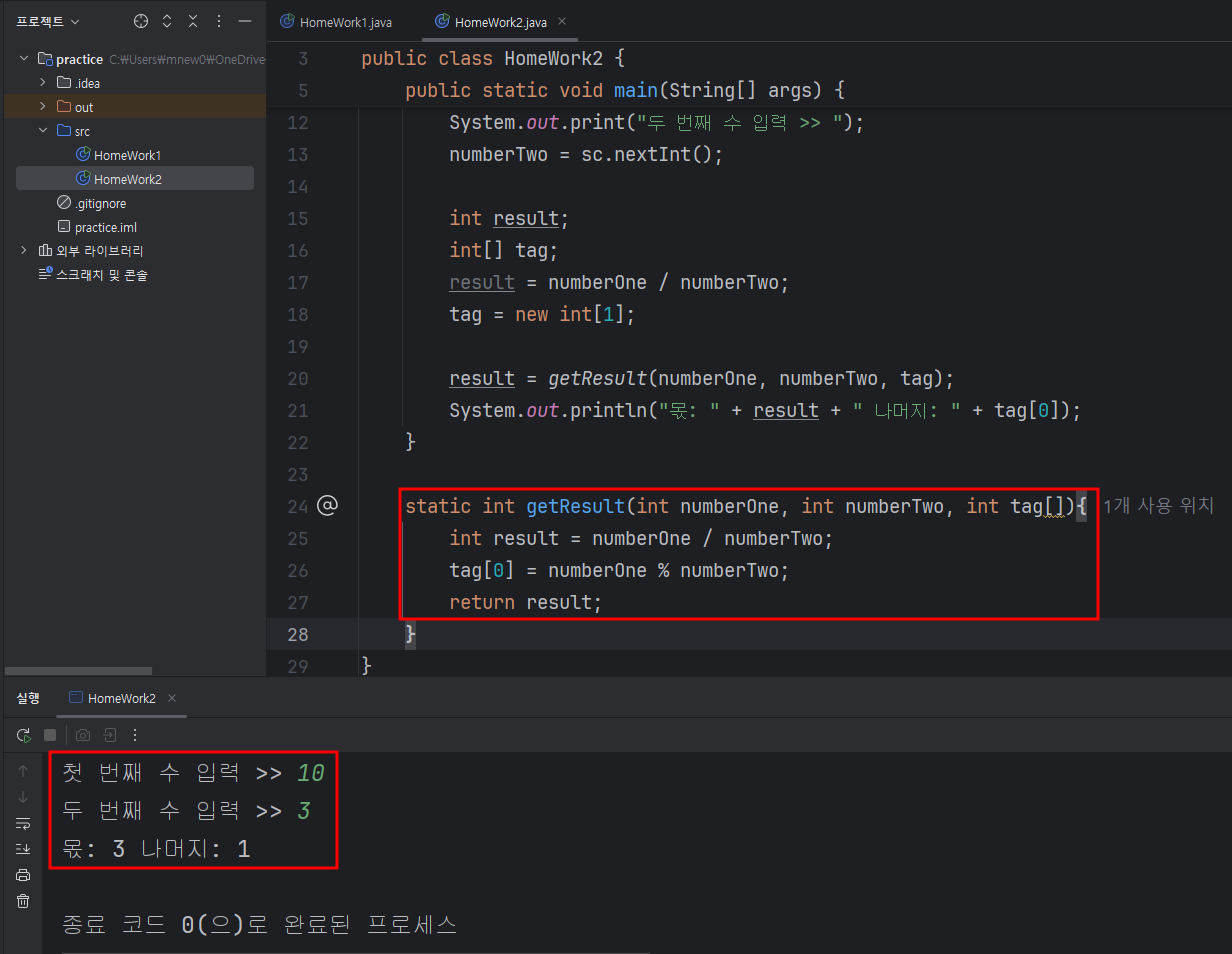
2.변수를 선언하고 두 수를 나눗셈 연산으로 몫과 나머지를 구하는 메소드를 작성하시오.
result = getResult(.... );
System.out.println("몫:" + result + " 나머지:" + tag[0]);
2번 문제 풀이
import java.util.Scanner;
public class HomeWork2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int numberOne, numberTwo;
System.out.print("첫 번째 수 입력 >> ");
numberOne = sc.nextInt();
System.out.print("두 번째 수 입력 >> ");
numberTwo = sc.nextInt();
int result;
int[] tag;
result = numberOne / numberTwo;
tag = new int[1];
result = getResult(numberOne, numberTwo, tag);
System.out.println("몫: " + result + " 나머지: " + tag[0]);
}
static int getResult(int numberOne, int numberTwo, int tag[]){
int result = numberOne / numberTwo;
tag[0] = numberOne % numberTwo;
return result;
}
}
3번. 두 점 (x, y)와 (x1, y1)간의 거리를 구하라.
// 루트함수: Math.sqrt
// ?승을 구하는 함수: Math.pow
double d = getDistance(1, 1, 2, 2);
System.out.println("두점의 거리는" + d + "입니다");
3번 문제 풀이
public class Homework3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double d = getDistance(1, 1, 2, 2);
System.out.println("두점의 거리는 " + d + " 입니다.");
}
static double getDistance(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2){
double d = Math.sqrt((Math.pow(y2 - y1, 2))+(Math.pow(x2-x1, 2)));
return d;
}
}
4번. 대문자로 변경하는 함수를 작성하라.
char[] ch = { 'a', 'b', 'c' }
UpperChar(ch)
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ch));
4번 문제 풀이
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Homework4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] ch = {'a', 'b', 'c'}; // a: 97, A: 65
UpperChar(ch);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ch));
}
static void UpperChar(char ch[]) {
for (int i = 0; i < ch.length; i++) {
int asc = (int)ch[i];
ch[i] = (char)(asc - 32);
}
}
}
5번. shuffle(섞는)메소드를 작성하시오. (random, swap 사용)
int[] original = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(original));
int[] result = shuffle(original);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(result));
5번 문제 풀이
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Homework5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] original = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(original));
int[] result = shuffle(original);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(result));
}
static int[] shuffle(int[] original){
for(int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) {
int x = (int) (Math.random() * 9); // 0 ~ 8까지 숫자가 하나 나옴.
int y = (int) (Math.random() * 9); // 0 ~ 8까지 숫자가 하나 나옴.
int temp = original[x];
original[x] = original[y];
original[y] = temp;
}
return original;
}
}
6번. max 메소드를 작성하시오.
int[] data = { 3, 2, 9, 4, 7 };
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(data));
System.out.println("최대값:"+ max(data));
6번 문제 풀이
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Homework6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] data = { 3, 2, 9, 4, 7 };
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(data));
max(data);
System.out.println("최댓값: "+ max(data));
}
static int max(int[] data){
int big = data[0];
for (int i = 0; i < data.length ; i++){
if( big < data[i] ){
big = data[i];
}
}
return big;
}
}
7번. 문자열에 숫자만 포함하고 있는지 문자가 포함되어 있는지 확인하는 isNumber메소드를 작성하시오
String str = "123";
System.out.println(str+"는 숫자입니까? "+ isNumber(str)); // true
str = "1234o";
System.out.println(str+"는 숫자입니까? "+ isNumber(str)); // false
str = "1a234";
System.out.println(str+"는 숫자입니까? "+ isNumber(str)); // false
7번 문제 풀이
public class Homework7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "123";
System.out.println(str+"는 숫자입니까? "+ isNumber(str));
str = "1234o";
System.out.println(str+"는 숫자입니까? "+ isNumber(str));
str = "1a234";
System.out.println(str+"는 숫자입니까? "+ isNumber(str));
}
static boolean isNumber(String str){
/*
String s = "hello";
for(int i = 0 ; i < s.length() ; i++ ){
char c = s.charAt(i); // String을 char로 한글자씩 산출
System.out.println("c = " + c);
}
*/
boolean b = true;
for(int i = 0 ; i < str.length() ; i++ ){
char c = str.charAt(i);
int asc = (int)c;
if(asc < 48 || asc > 57){
b = false;
break;
}
}
return b;
}
}
8번. 2차원 배열을 1차원 배열로 변환하는 함수를 작성하라.
int arrayTwo[][] = {
{ 1, 2, 3, 4 },
{ 5, 6, 7, 8 },
{ 9, 10, 11, 12 },
};
int arrayOne( arrayTwoOne );
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(arrayTwoOne) );
8번 문제 풀이
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Homework8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 8. 2차원 배열을 1차원 배열로 변환하는 함수를 작성하라.
int arrayTwo[][] = {
{ 1,2,3,4 }, // arrayTwo.length
{ 5,6,7,8 }, // arrayTwo[n].length
{ 9,10,11,12 },
}; // → { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12 }
int arrayOne[] = arrayTwoOfArrayOne( arrayTwo );
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arrayOne));
}
static int[] arrayTwoOfArrayOne(int[][] arrayTwo){
int[] arrayOne = new int[arrayTwo.length * arrayTwo[0].length];
// 첫 번째 방법
/* for(int i = 0 ; i < arrayTwo.length ; i++ ){
for(int j = 0; j < arrayTwo[i].length ; j++){
arrayOne[(arrayTwo[i].length * i) + j ] = arrayTwo[i][j];
}
}
return arrayOne;*/
// 두 번째 방법
int count = 0;
for(int i = 0 ; i < arrayTwo.length ; i++ ) {
for (int j = 0; j < arrayTwo[i].length; j++) {
arrayOne[count] = arrayTwo[i][j];
count++;
}
}
return arrayOne;
}
}
'JAVA 프로그래밍' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [JAVA] 풀스택 개발자 부트캠프 007일차 ② 예외 처리(Exception) (0) | 2025.01.02 |
|---|---|
| [JAVA] 풀스택 개발자 부트캠프 007일차 ① 함수로 나타내기 (0) | 2025.01.02 |
| [JAVA] 풀스택 개발자 부트캠프 006일차 ③ value(값), address(주소)의 할당 (1) | 2024.12.31 |
| [JAVA] 풀스택 개발자 부트캠프 006일차 ② 대문자를 소문자로 바꾸는 함수 (0) | 2024.12.31 |
| [JAVA] 풀스택 개발자 부트캠프 006일차 ① function(함수) (0) | 2024.12.31 |